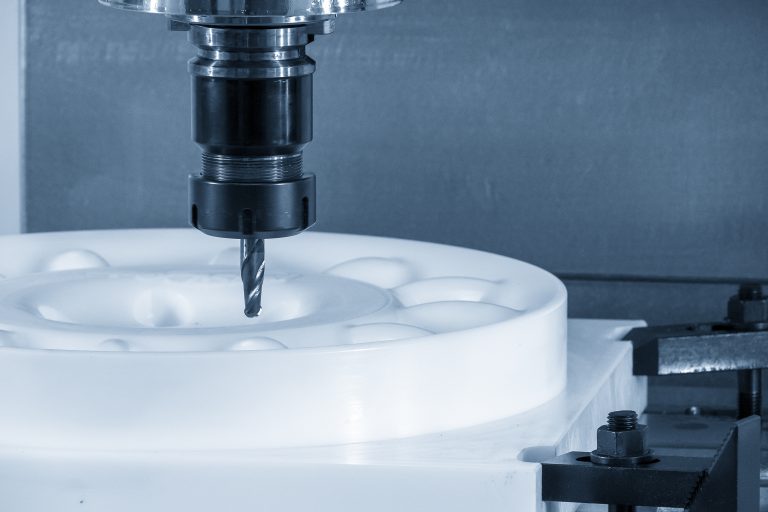
D2 Steel Machined Parts:Unleashing the Power of Precision
D2 Steel Machined Parts:Unleashing the Power of Precision What is D2 Steel? D2 Tool Steel is classified as high carbon tool steel due to its high carbon content, typically raning from 1.40% to 1.60%. It falls under the cold-work tool steel category. D2 tool steel is an ideal choice for precision machining applications thanks to its exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and dimensional stability. What are the Typical Chemical Composition of D2 Steel? The typical chemical composition of D2 Tool Steel includes: The typical chemical composition of D2 Tool Steel Carbon(C) Chromium(Cr) Vanadium(V) Molybdenum(Mo) Silicon(Si) Manganese(Mn) 1.40%-1.60% 11.00%-13.00% 0.70%-1.20% 0.70%-1.20% 0.10%-0.60% 0.10%-0.60% Some Names of Steel D2 Commonly Used Worldwide D2 tool steel goes by various names across the globe. Some of the well-known names include: – AISI D2 Steel: This is the standard designation…