What is Injection Molding?–Definition, Types, and Materials
What is Injection Molding? And How does Injection Mold work?
Injection molding (or Injection Moulding) is a manufacturing process used to produce parts and products by injecting molten material into a injection mold cavity. The process typically involves the following steps:
Clamping:
The two halves of the mold, the stationary side, and the moving side are securely closed together under high pressure. This creates a sealed mold cavity.
Injection:
Molten material, usually in the form of thermoplastics, is injected into the mold cavity through a injection molding nozzle. The material fills the cavity, taking its shape and conforming to the mold’s contours.
Cooling:
After the material is injected, it is allowed to cool and solidify within the mold. Cooling time depends on the material and part design.
Ejection:
Once the material has solidified, the mold is opened, and the part is ejected using injection molding ejector pins or other mechanisms.
Cycle Repeat:
The process is repeated for subsequent parts, allowing for high-volume production.
How to Reduce Injection Mold cost?What shall you to Considerate in Using Injection Molding?
Several considerations should be taken into account when deciding to use injection molding for a specific project
Cost:
Injection molding can be cost-effective for large production runs due to its high initial setup costs but low per-unit cost.
Production Quantity:
Injection molding is ideal for high-volume production, as the cycle time per part is relatively short.
Design Factors:
Part design plays a crucial role in successful injection molding. Design considerations include draft angles for injection molding, injection molding wall thickness, gate location in injection molding, and the use of injection molding ribs and injection molding fillets to enhance structural integrity.
Production Considerations:
injection molding materials selection, injection molding tooling design, and machine capacity are essential factors in the production process.
How to Reduce Injection Mold cost?
How much does an injection mold cost? It depends on the mold itself, but you can consider the following strategies to reduce injection mold costs :
- Simplify the part design to minimize complexity and tooling requirements.
- Optimize the injection mold design for easier manufacturing and reduced material waste.
- Collaborate with experienced mold designers and manufacturers who can suggest cost-saving solutions.
- Utilize cost-effective materials that meet the required specifications.
When is Injection Molding Used?
Injection molding is commonly used when:
- Large quantities of parts are required.
- Complex part geometries need to be achieved.
- High precision and tight tolerances are necessary.
- Repeatable and consistent part quality is essential.
- Cost-effective production is needed for long production runs.
What are the Types of Injection Molding Process?
What are the Types of Injection Molding Process?
- Conventional Injection Molding: also known as traditional injection molding, refers to the standard and most widely used method of injection molding.
- Two-Shot Injection Molding: A process that enables the production of parts with two different materials or colors in a single mold cycle.
- Insert Molding Injection: Involves inserting pre-formed components or inserts into the mold before the injection process.
- Multi-Shot Injection Molding: Allows for the injection of multiple materials or colors in a sequential or simultaneous manner.
What Materials can be Injection Molded?
A wide range of materials can be used in injection molding, including metals (the process is called die casting), glass, elastomers, confectionery, and most commonly thermoplastic and thermosetting ployoers. The material selection depends on the desired properties, part requirements, and application.
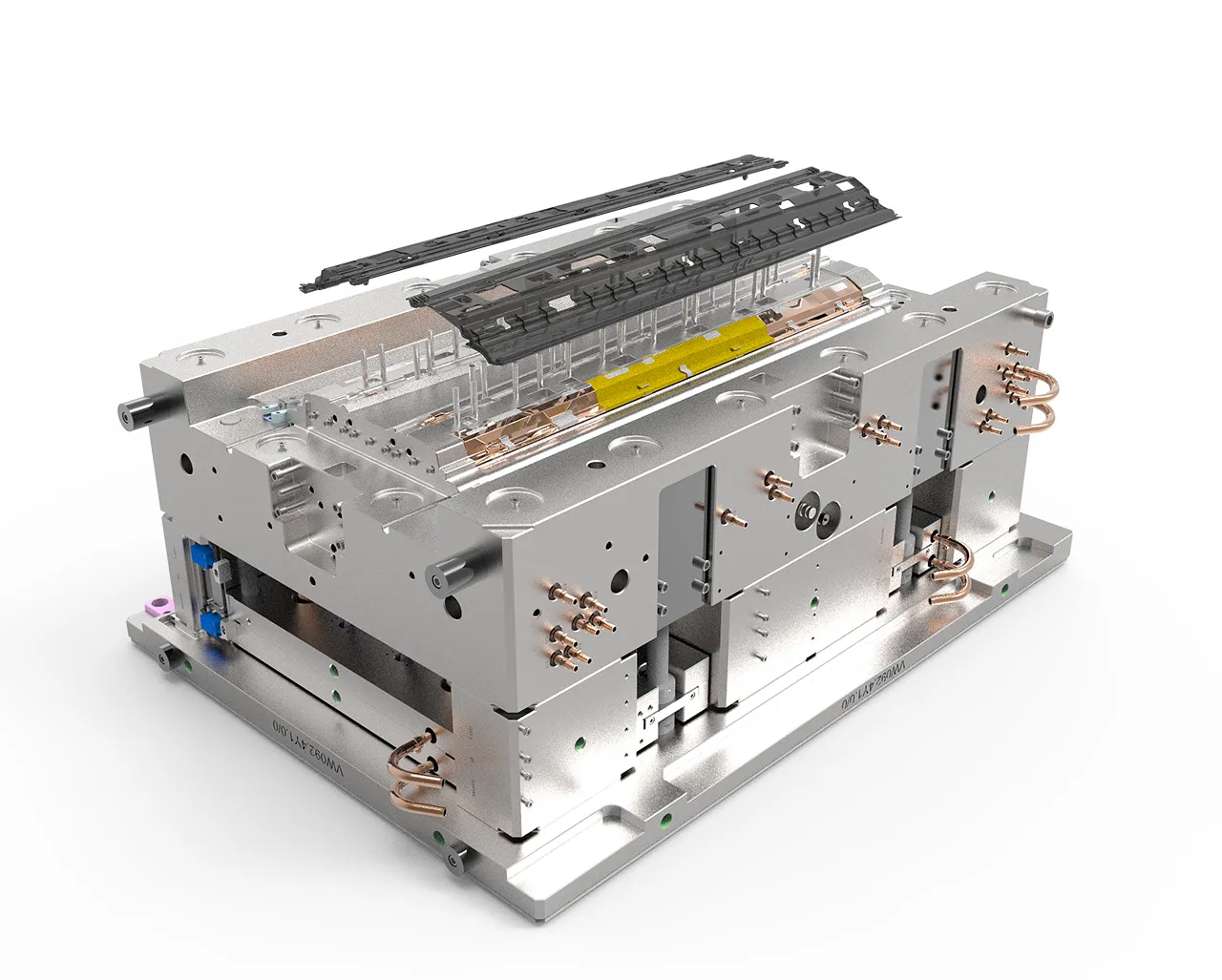
What are the Benefits of Injection Molding?
Injection molding offers several advantages, including:
- High production efficiency and repeatability
- Wide range of material options
- Complex part geometries and intricate details
- High precision and tight tolerances
- Minimal post-processing required
- Cost-effective for large production runs
What are the Disadvantages of Injection Molding?
Some disadvantages of injection molding include:
- High initial tooling and setup costs
- Longer lead time for mold fabrication
- Limited flexibility for design changes once the mold is produced
- Not suitable for small production runs or prototyping
What are the Applications of Injection Molded Parts and Injection Molding Products?
Injection molding applications can be found in various industries, including:
- Injection Molding Automotive Parts: Interior and exterior injection molding components, injection molded electrical connectors, and under-the-hood parts.
- Injection Molded Consumer Products: Household appliances, packaging, toys, and injection molding electronics.
- Medical Injection Molding: Injection molding medical devices, disposable items, and diagnostic equipment.
- Aerospace Injection Molding: Interior components, connectors, and structural parts.
- Industrial Injection Molding: Custom injection molded enclosures, injection molded gears, injection molded knobs, and machinery components.
Injection Molding Services from U-Need
Injection molding is a versatile and efficient manufacturing process used to produce a wide range of parts and products. By considering factors such as design, material selection, and production quantity, injection molding can be a reliable and economical solution for your manufacturing needs.
If you are in need of high-quality parts or products made using injection molding, even design for injection molding, look no further than U-Need. Contact us or send E-mail: info@uneedpm.com today to discuss your specific requirements and how we can assist you in achieving your manufacturing goals.
